What’s the most complex problem you have solved recently
- Helped sort out inventory
Breaking things down into smaller problems will make the overall problem seem easier.
What is First Principles Thinking?
Breaking down complex problems down into their most basic, fundamental parts. It’s about questioning assumptions and building from the ground up.
Why is this necessary?
We rely on existing solutions and analogies can limit our creativity. FPT forces us to look at problems differently and find unique solution.
At Tesla, Elon and team asked a fundamental questions about the cost of batteries and found ways to reduce them significantly.
At SpaceX, Elon asked why are rockets expensive and designed reusable rockets, drastically cutting costs.
What other forms of thinking are there?
Analogous Thinking
FPT vs Analogous Thinking
AT: Drawing parallels from similar situations or using existing solutions and experiences as references. FPT: Breaking down complex problems into their most fundamental elements and building solutions from these basic truths
AT: Often leads to incremental innovation and improvements where as FPT encourages radical innovation
Risk is low in AT and high in FPT
Speed in AT is high in short term and opposite in FPT
Use case for AT: Enhancing a project management tool by adding features similar to those in competitor tools Use case for FPT: Redesigning a project management tool by questioning the fundamental needs of project managers and creating a tool that addresses
Products with and without FPT
- Apple iPhone vs BlackBerry
- Google Search vs Yahoo Search
- Dropbox vs Microsoft OneDrive
- Slack vs MSFT Teams
- Nest Thermostat vs Traditional Programmable Thermostats
- WhatsApp vs Skype
Are there any cases where analogous thinking is essential?
- Mature and stable processes: established and efficient processes that have been optimized over time
- Compliance and regulatory requirements: situation governed by strict compliance and regulator requirements
- Time sensitive & resource constrains: projects with tight deadlines
- High risk environments: Environments where experimentation carries a significant risk
- Legacy systems: Integrating with legacy systems that have specific constraints and deps
- Well established product: features that are well-established, widely used and critical to the product
Don’t let your thought process be limited by the time and resource constraints. Take the analogous approach now and then down the road, adopt FPT
Case Study - Part 1
Imagine you’re the product manager for a new app aimed at improving remote work productivity.
Despite having several useful features, user engagement is low, and the app is not gaining traction.
What would you do.
Steps to apply FPT
- Identify the problem
- Clearly definet he porbelm
- Break ir down
- Deconstruct to fundamentals
- Ask why, what to get to the root cause or fundamental elements of the problem
- Challenge assumptions and stripo away any preconceived notions or biases
- Reconstruct from the ground up
- Once you have id the basic elements, start to build up solutions from these fundamentals
- Combine these basic elements in new ways to develop innovative solutions.
Frameworks for deconstructing to fundamentals
F1 - Five Why’s? F2: The Four Thing Question F3 First Principles Laddering F4: Contrarian Questioning F5: Mind Mapping
RICE - look it up for the mind map
Five Why’s Framework
By repeatedly asking why you can uncover the root cause of the problem.
This method ensures we address the root cause and not just the symptoms
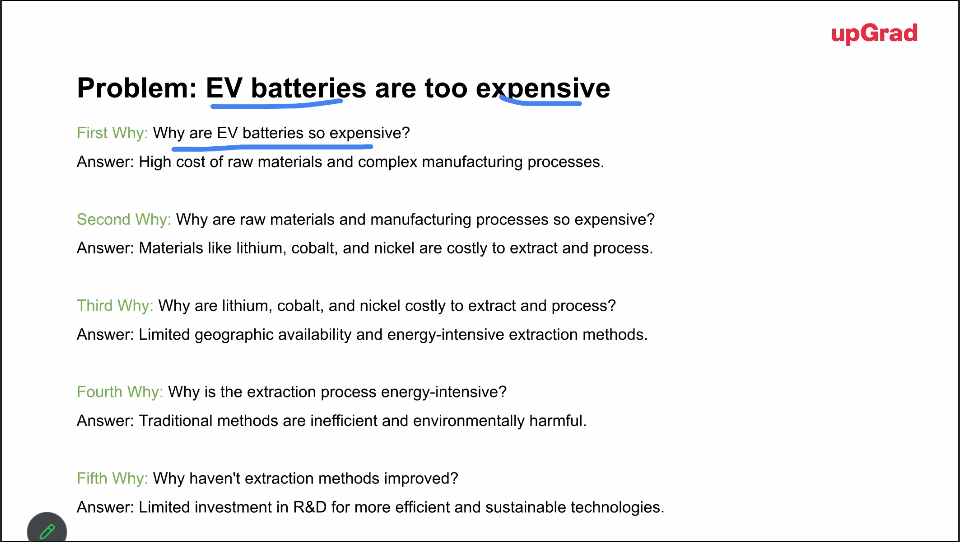
It can be three whys or five, as long as you arrive at the most fundamental approach.
The Four Thing Question
What is the problem? Why is it the problem? What is the solution? Why is it the solution?
Part 2 - Case Study
Why is the remote productivity app’s engagement low?
Because it might not keep the users interested enough
Why does it not keep the users interested enough?
Because it might be that the users are not finding the features helpful enough
Why are they not finding the features helpful enough?
They are too wide spread in order to fully help in increasing the productivity
Why are the features too wide?
They need to be better defined as per the core problems that need to be solved


Waymo Case Study


 Contrarian thinking
Contrarian thinking

Tying it all together for PMs
- Cultivate a curious mindset - always ask question and seek to understand the fundamental princples behind everything you encounter.
- Break down problems - decompose problems into their components instead of tackling them as whole entities
- Challenge Assumptions - regularly question the assumptions that you and you team make
- Use Structured Frameworks - apply frameworks like Five Why, SWOT analysis, and mind mapping to systematically analyze problems and solutions
- Adopt a learning mentality - embrace continuous learning and improvement
- Simplify complexity - strive to simplify complex problems and solutions
- Leverage data and analytics
- Collaborate and brainstorm
- Develop hypotheses and test them
- Reflect and Iterate - regularly reflect on your decisions and their outcomes and be prepared to iterate based on what you learn.